|
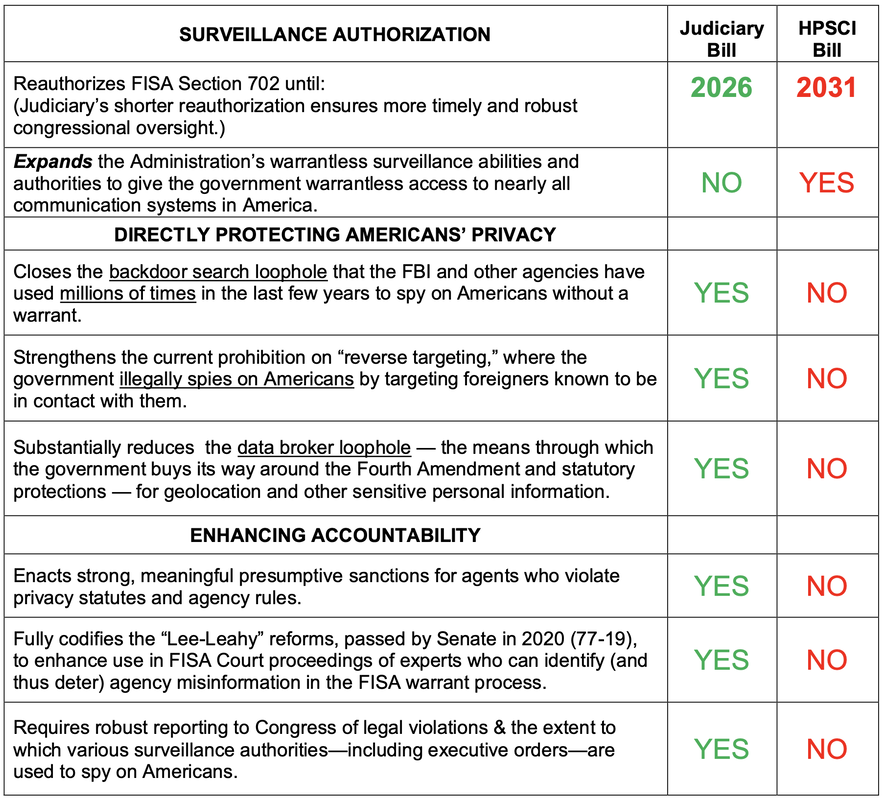
When Members of the House voted last week to reauthorize FISA Section 702, most did not realize that an amendment from the House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence (HPSCI), sold as a “narrow” definitional change to the law, will actually deliver what Sen. Ron Wyden (D-OR) calls “one of the most dramatic and terrifying expansions of government surveillance authority in history.” What the House missed the Senate can still fix. The Senate still has time to perform emergency surgery and excise this particularly toxic amendment. Here’s the background: For years, “electronic communications service providers” such as Verizon or Google’s Gmail have been required to turn over the communications of targets. The House bill expands this requirement to enlist millions of small businesses that provide Wi-Fi or have access to routers or similar communications equipment. This provision would make American small businesses into providers of KGB-like surveillance. If this seems hyperbolic, consider that this HPSCI amendment would force American small businesses of many sorts to collect the communications of their customers for the government. The bill does this by including any service provider who has access to equipment that transmits communications. The language was narrowed to exclude hotels, restaurants, dwellings, and community centers, but the measure still includes most businesses – owners and operators of any facilities that house equipment used to store or carry data, including data centers and commercial office buildings. Millions of Americans, with little or no knowledge of the equipment they own or service –landlords, utility providers, repairmen, plumbers, cleaning contractors, and similar professionals – would have a legal obligation to secretly spy for the government. Lacking any ability to separate the communications of Americans from foreigners, they would be forced either to give the government direct access to the equipment or copy its messages en masse and turn it over. And then they would be under a gag order to keep their snooping a secret. This version of Section 702 reauthorization would be a disaster for small businesses of all sorts. Bound to silence, small businesses would suffer consumer distrust as public knowledge of the contamination of the data supply chain spread. Consumers and business would have no recourse. This bill also marks a terrifying replacement of the constitutional order under the Fourth Amendment. For these reasons, the Senate must do its duty and remove it. Call Your Senators: |
Categories
All
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed